Cell Isolation Systems for Cell Separation
Cell isolation products enable the separation and recovery of specific cell types from complex samples such as blood, tissue, or culture. This process is essential for establishing cell cultures and conducting targeted analyses. The single-cell isolation method allows researchers to separate individual cells from heterogeneous populations for precise downstream analysis. Cell separation methods commonly employ fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS), magnetic separation, or microfluidics. Leveraging these approaches, a range of instruments for high throughput cell sorting and dispensing, separator devices, and kits with supporting reagents from multiple suppliers are available. These tools support diverse applications, including blood component volume reduction, enrichment of mononuclear cells from cord blood, bone marrow concentration, and single-cell dispensing. Related flow cytometry products are also available for the isolation of organelles, such as mitochondria, nuclei, and the endoplasmic reticulum.read more
Key Features of Cell Separation Technologies
- Magnetic cell separation with paramagnetic microspheres provides high yields of pure, viable, and functional cells. This approach also reduces process steps, saving time while maintaining excellent cell viability.
- The systems support both positive and negative selection strategies to suit different experimental goals. Positive selection directly captures the target cells, while negative selection removes unwanted cells, leaving the cells of interest with high purity.
- The only fully closed cell isolation platform is designed for GMP-compliant cell production and sorting applications. Its innovative design combines superior cell isolation performance with ease of use and seamless scalability from process development to full production.
- Unlike traditional flow cytometers, it supports multi-marker selection, enabling precise identification and isolation of target immune cells. This approach improves purity, eliminates non-target or ineffective cells, and maintains high cell viability.
- The system is optimized for use in research, process development, and manufacturing environments related to ATMP and regenerative medicine. It is specifically intended for ex vivo cell separation processing and is not sold as a medical device for direct therapeutic or diagnostic use.
- Designed with GMP compliance in mind, it overcomes the complexity and limitations of conventional flow cytometers. It minimizes cell stress or damage during sorting and offers a reliable, production-ready solution for advanced cell and gene therapy workflows.
Applications of Cell Isolation and Separation Methods
- Cell and gene therapy: Isolated cells can be expanded, genetically modified, and reinfused into patients as part of advanced therapeutic approaches. These therapies rely on the precise selection of functional and viable cells to achieve clinical efficacy.
- Immunology research: Isolation of immune cell subsets, such as T cells, B cells, or NK cells, enables a detailed study of immune responses. This supports vaccine development, autoimmune disease research, and immunotherapy design.
- Stem cell research: Stem cells can be isolated from bone marrow, cord blood, or other tissues for use in regenerative medicine. Pure populations of stem cells are essential for studying differentiation and developing therapeutic applications.
- Cancer research: Circulating tumor cells and other cancer-associated cell types can be separated for molecular analysis. This helps in early detection, biomarker discovery, and the development of targeted cancer therapies.
- Transplantation and regenerative medicine: Isolation of viable cells enhances the success of bone marrow transplants and other cell-based treatments. These systems support the preparation of cells that can aid in tissue repair and regeneration.
- Microbiology and infectious disease research: Cell isolation systems can separate host cells from pathogens or isolate specific microbial populations. This supports studies on host–pathogen interactions and the development of antimicrobial therapies.
- Neuroscience research: Neurons, glial cells, and other brain-derived cell types can be isolated to study neural function and disease mechanisms. These applications are critical for advancing research in neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s disease.
- Drug discovery and toxicology: Isolated cells provide reliable models for screening drug candidates and evaluating toxicity. High-purity cell populations ensure accurate, reproducible results in preclinical testing.
- Single-cell analysis: The single-cell isolation technique is essential for single-cell sequencing, transcriptomics, and proteomics. This enables detailed characterization of cellular heterogeneity within complex tissues.
- Prenatal and reproductive medicine: Rare fetal cells or gametes can be isolated from maternal blood or reproductive tissues. These methods assist in non-invasive prenatal testing and fertility research.
Showing the single result
Category
- Bioreactors+
- Parallel Bioreactors
- Single-Use Bioreactors
- Stirred-Tank Bioreactors
- Capillary Electrophoresis Instruments+
- Capillary Gel Electrophoresis (CGE)
- Capillary Isoelectric Focusing (CIEF)
- Capillary Zone Electrophoresis (CZE)
- Cell Counters and Analyzers+
- Automated Cell Counters
- Manual Cell Counters
- Cellular Imaging Systems+
- Fluorescence Imaging Systems
- High-Content Imaging Systems
- Live-Cell Imaging Systems
- Centrifuges+
- Benchtop Centrifuges
- Clinical Centrifuges
- Micro Centrifuges
- Refrigerated Centrifuges
- Ultracentrifuges
- Chromatography Instruments+
- Gas Chromatography
- Ion Chromatography
- Liquid Chromatography
- Flow Cytometer+
- Cell Analyzers
- Cell Isolation Systems
- Cell Sorters
- High-Throughput Flow Cytometers
- Imaging Flow Cytometry
- Personal Flow Cytometers
- Portable/Benchtop Flow Cytometers
- Spectral Flow Cytometers
- Laboratory Incubators+
- CO2 Incubators
- Dry Bath Incubators
- Hypoxia Incubators and Chambers
- Incubator Shakers
- Laboratory Ovens
- Portable Incubators
- Thermal Mixers
- Laboratory Microscopes+
- Atomic Force Microscopes (AFM)
- Automated Modular Microscopes
- Compound Microscopes
- Confocal Microscopes
- Digital Microscopes
- Fluorescence Microscopes
- Inverted Microscopes
- Live Cell Imaging Microscopes
- Metallurgical Microscopes
- Multiphoton Microscopes
- Polarizing Microscopes
- Raman Microscopes
- Scanning Electron Microscopes (SEM)
- Stereo Microscopes
- Super-Resolution Microscopes
- Transmission Electron Microscopes (TEM)
- Upright Microscopes (Neuroscience)
- Liquid Handlers+
- Automated Pipetting Systems
- Multi-Channel Liquid Handlers
- Robotic Liquid Handlers
- Variable Volume Pipetting Systems
- Mass Spectrometers+
- Ambient Ionization
- APCI MS
- ESI MS
- FT ICR MS
- ICP MS
- Orbi Trap MS
- Quadrupole MS
- Time-of-Flight MS
- Microarray Scanners+
- DNA Microarray Scanners
- Laser-Based Microarray Scanners
- Microplate Readers+
- Absorbance Microplate Readers
- Fluorescence Microplate Readers
- Luminescence Microplate Readers
- Multimode Microplate Readers
- Particle Counters and Analyzers+
- Airborne Particle Counters
- Laser Diffraction Analyzers
- Liquid Particle Counters
- Nanoparticle Analyzers
- Portable Particle Counters
- Remote Particle Counters
Brand
- ACCU-SCOPE
- Agilent
- Airmodus
- Alphasense
- Analytik Jena
- ARGO-HYTOS
- Arrayit
- Aurora Biomed Inc.
- Azure Biosystems
- Baker
- BD Biosciences
- Beckman Coulter
- Beijing Challen Biotechnology
- Binder
- Bio-Techne
- Biobase
- BioRad
- BMG Labtech
- Bruker
- Celestron
- Cellbox
- Centurion Scientific Ltd
- ChemoMetec
- CleanAir
- Cleatech
- Corning
- Countstar
- CS Instruments
- CUBIC
- Cytek Biosciences
- Cytena
- Cytiva
- Data Technologies
- Descase
- Electrolab Biotech
- Eppendorf
- Euromex
- Evident
- Fermex
- Fluke
- Formulatrix
- Getinge
- Gilson
- GPC Bio
- Haier Biomedical
- Hamilton Company
- Hettich
- Hitachi High-Tech
- Hudson Robotics Inc.
- Hydro
- INFORS HT
- Innopsys
- Jasco
- Jeiotech
- JEOL
- Kanomax
- Keyence
- KNAUER
- LAB-KITS
- Labomed
- Labwit
- Leco
- Leica
- Lighthouse
- Logos Biosystems
- LOSI
- Lumex Instruments
- Luminex
- Malvern Panalytical
- Meiji Techno
- Memmert
- Merck
- Mettler-Toledo International Inc.
- Miltenyi Biotec
- Molecular Devices
- Motic
- MP Filtri
- MSE (Medical and Scientific Equipment)
- NCI
- Nikon Instruments
- NuAire
- ORFLO Technologies
- Oxford Instruments
- PAMAS
- Particle Measuring Systems
- Particles Plus
- PBS Biotech
- PCE instruments
- PerkinElmer
- PharSol
- PHCbi
- Prior Scientific
- Promega
- Qiagen NV
- Revvity
- RION
- Sartorius
- SATAKE
- Sciex
- Sebia
- SETA
- Setra
- Shimadzu
- SIBATA
- Sigma Laborzentrifugen GmbH
- Solaris Biotech
- Solida Biotech
- Sony Biotechnology Inc.
- SPT Labtech Ltd
- Stratedigm Inc.
- Sysmex Corporation
- Tecan
- TES
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- TSI
- Waters
- Western States Machine Company
- ZEISS
- ZETRON
-
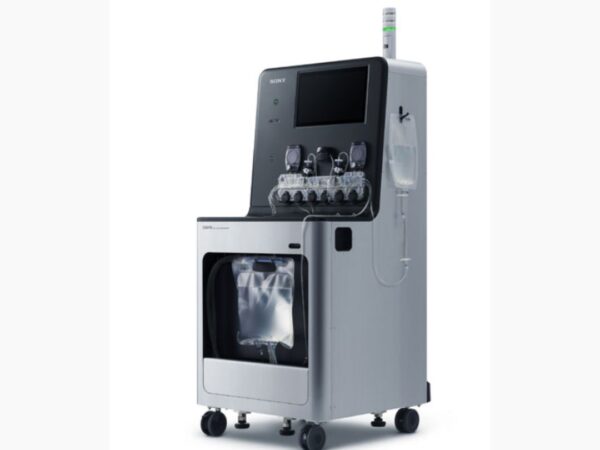
Sony Biotechnology Inc. CGX10 Cell Isolation System
CGX10 offers gentle isolation of single cells or clusters using microchip-based flow channels.