Atomic Force Microscopes (AFM): Advanced Nanoscale Imaging Solutions
Atomic force microscopes (AFM) represent one of the most versatile and powerful tools for nanoscale analysis in modern life sciences and materials research. These sophisticated atomic force microscopy systems enable researchers to capture three-dimensional topographic images with exceptional precision, achieving atomic resolution with Ångström-level height accuracy. Unlike traditional microscopy techniques, the atomic force microscopy technique requires minimal sample preparation while delivering unparalleled insights into surface properties and intermolecular forces.read more
The AFM microscope operates by scanning a sharp cantilever tip across a sample surface, measuring deflections caused by atomic forces between the probe and specimen. This atomic force microscope function allows scientists to visualize structures at resolutions beyond the capabilities of optical microscopy, making it indispensable for examining biological samples, nanomaterials, and molecular structures. The atomic force microscopy machine’s ability to operate in ambient conditions, controlled environments, or liquid media makes it particularly valuable for life sciences applications where sample integrity must be preserved. Whether imaging soft biological tissues, characterizing material properties, or performing single-molecule force spectroscopy, atomic force microscopy instrumentation continues to expand the boundaries of scientific investigation at the nanometer scale.
Key Features
Atomic force microscopy systems offer distinctive capabilities that establish them as essential instrumentation for nanoscale research:
- Atomic-level resolution: AFM microscopes achieve exceptional atomic force microscopy resolution, capable of imaging individual atoms and distinguishing between different atomic species on surfaces through chemical bond interactions.
- Three-dimensional imaging: These systems generate comprehensive topographic maps that reveal surface features in three dimensions, providing detailed height and spatial information beyond two-dimensional imaging techniques.
- Versatile operational modes: The best atomic force microscope platforms feature multiple scanning modes including contact mode, tapping mode, and frequency modulation, each optimized for different sample types and measurement requirements.
- Force measurement capabilities: Beyond imaging, atomic force microscopy systems measure intermolecular forces, mechanical properties, and elastic moduli through force spectroscopy applications.
- Minimal sample preparation: Unlike electron microscopy techniques that require extensive preparation, AFM atomic force microscopy allows direct examination of samples in their native states without stains or contrast agents.
- Multi-environment compatibility: Atomic force microscope working conditions span ultra-high vacuum, ambient atmospheric conditions, and liquid environments, enabling biological sample analysis in physiologically relevant conditions.
- Nanomechanical characterization: Advanced atomic force microscopy instrumentation quantifies chemical, mechanical, electrical, and magnetic material properties with nanometer resolution.
Applications of Atomic Force Microscopes
Atomic force microscopes serve diverse research applications across multiple scientific disciplines:
- Life sciences and biomedical research: AFM technology enables nanoscale imaging of biological materials including cells, proteins, and DNA structures in both ambient and liquid environments, supporting cancer diagnostics, drug discovery, and mechanobiology studies.
- DNA visualization and analysis: Atomic force microscopy provides efficient, cost-effective methods for visualizing DNA constructs directly on substrates, completing imaging from sample to final image in under 30 minutes for quality control applications.
- Materials science and nanotechnology: Researchers employ atomic force microscopy machines to characterize surface properties of the sample, measure nanoscale features, and analyze material compositions with sub-nanometer precision
- Single-molecule force spectroscopy: The atomic force microscopy technique investigates mechanical properties of biomolecules, cellular responses to mechanical forces, and fundamental biological processes such as cell division.
- Virology and infection research: AFM microscopes track mechanical changes in viral particles during infection processes, providing insights into pathogen behavior at the molecular level.
- Neuroscience applications: Atomic force microscopy systems address questions about mechanosensing mechanisms in neurons and cellular mechanical responses.
Showing all 12 results
Category
- Bioreactors+
- Parallel Bioreactors
- Single-Use Bioreactors
- Stirred-Tank Bioreactors
- Capillary Electrophoresis Instruments+
- Capillary Gel Electrophoresis (CGE)
- Capillary Isoelectric Focusing (CIEF)
- Capillary Zone Electrophoresis (CZE)
- Cell Counters and Analyzers+
- Automated Cell Counters
- Manual Cell Counters
- Cellular Imaging Systems+
- Fluorescence Imaging Systems
- High-Content Imaging Systems
- Live-Cell Imaging Systems
- Centrifuges+
- Benchtop Centrifuges
- Clinical Centrifuges
- Micro Centrifuges
- Refrigerated Centrifuges
- Ultracentrifuges
- Chromatography Instruments+
- Gas Chromatography
- Ion Chromatography
- Liquid Chromatography
- Flow Cytometer+
- Cell Analyzers
- Cell Isolation Systems
- Cell Sorters
- High-Throughput Flow Cytometers
- Imaging Flow Cytometry
- Personal Flow Cytometers
- Portable/Benchtop Flow Cytometers
- Spectral Flow Cytometers
- Laboratory Incubators+
- CO2 Incubators
- Dry Bath Incubators
- Hypoxia Incubators and Chambers
- Incubator Shakers
- Laboratory Ovens
- Portable Incubators
- Thermal Mixers
- Laboratory Microscopes+
- Atomic Force Microscopes (AFM)
- Automated Modular Microscopes
- Compound Microscopes
- Confocal Microscopes
- Digital Microscopes
- Fluorescence Microscopes
- Inverted Microscopes
- Live Cell Imaging Microscopes
- Metallurgical Microscopes
- Multiphoton Microscopes
- Polarizing Microscopes
- Raman Microscopes
- Scanning Electron Microscopes (SEM)
- Stereo Microscopes
- Super-Resolution Microscopes
- Transmission Electron Microscopes (TEM)
- Upright Microscopes (Neuroscience)
- Liquid Handlers+
- Automated Pipetting Systems
- Multi-Channel Liquid Handlers
- Robotic Liquid Handlers
- Variable Volume Pipetting Systems
- Mass Spectrometers+
- Ambient Ionization
- APCI MS
- ESI MS
- FT ICR MS
- ICP MS
- Orbi Trap MS
- Quadrupole MS
- Time-of-Flight MS
- Microarray Scanners+
- DNA Microarray Scanners
- Laser-Based Microarray Scanners
- Microplate Readers+
- Absorbance Microplate Readers
- Fluorescence Microplate Readers
- Luminescence Microplate Readers
- Multimode Microplate Readers
- Particle Counters and Analyzers+
- Airborne Particle Counters
- Laser Diffraction Analyzers
- Liquid Particle Counters
- Nanoparticle Analyzers
- Portable Particle Counters
- Remote Particle Counters
Brand
- ACCU-SCOPE
- Agilent
- Airmodus
- Alphasense
- Analytik Jena
- ARGO-HYTOS
- Arrayit
- Aurora Biomed Inc.
- Azure Biosystems
- Baker
- BD Biosciences
- Beckman Coulter
- Beijing Challen Biotechnology
- Binder
- Bio-Techne
- Biobase
- BioRad
- BMG Labtech
- Bruker
- Celestron
- Cellbox
- Centurion Scientific Ltd
- ChemoMetec
- CleanAir
- Cleatech
- Corning
- Countstar
- CS Instruments
- CUBIC
- Cytek Biosciences
- Cytena
- Cytiva
- Data Technologies
- Descase
- Electrolab Biotech
- Eppendorf
- Euromex
- Evident
- Fermex
- Fluke
- Formulatrix
- Getinge
- Gilson
- GPC Bio
- Haier Biomedical
- Hamilton Company
- Hettich
- Hitachi High-Tech
- Hudson Robotics Inc.
- Hydro
- INFORS HT
- Innopsys
- Jasco
- Jeiotech
- JEOL
- Kanomax
- Keyence
- KNAUER
- LAB-KITS
- Labomed
- Labwit
- Leco
- Leica
- Lighthouse
- Logos Biosystems
- LOSI
- Lumex Instruments
- Luminex
- Malvern Panalytical
- Meiji Techno
- Memmert
- Merck
- Mettler-Toledo International Inc.
- Miltenyi Biotec
- Molecular Devices
- Motic
- MP Filtri
- MSE (Medical and Scientific Equipment)
- NCI
- Nikon Instruments
- NuAire
- ORFLO Technologies
- Oxford Instruments
- PAMAS
- Particle Measuring Systems
- Particles Plus
- PBS Biotech
- PCE instruments
- PerkinElmer
- PharSol
- PHCbi
- Prior Scientific
- Promega
- Qiagen NV
- Revvity
- RION
- Sartorius
- SATAKE
- Sciex
- Sebia
- SETA
- Setra
- Shimadzu
- SIBATA
- Sigma Laborzentrifugen GmbH
- Solaris Biotech
- Solida Biotech
- Sony Biotechnology Inc.
- SPT Labtech Ltd
- Stratedigm Inc.
- Sysmex Corporation
- Tecan
- TES
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- TSI
- Waters
- Western States Machine Company
- ZEISS
- ZETRON
-
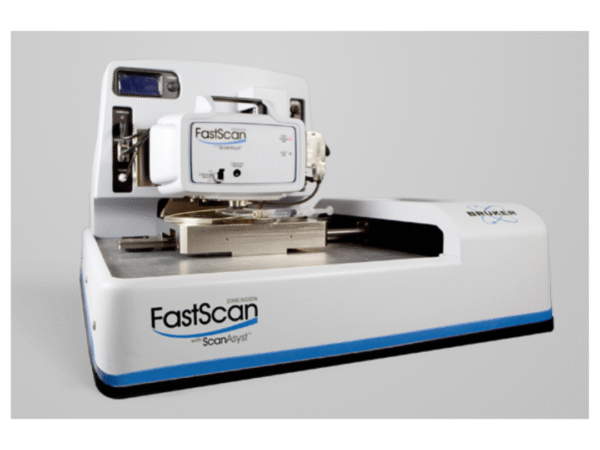
Bruker Dimension FastScan Bio
FastScan Bio provides real-time AFM imaging of live cells with sub-molecular resolution and speed.
-
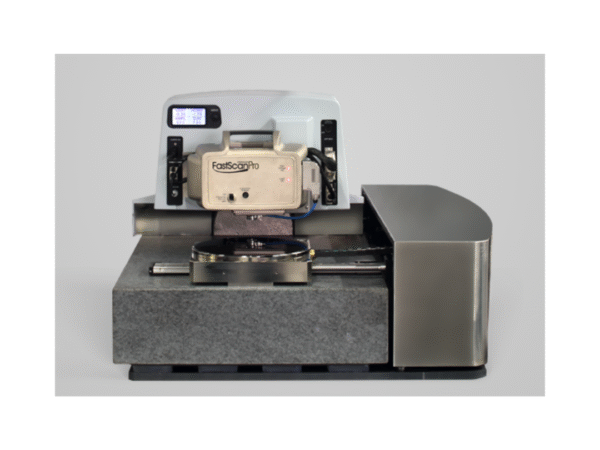
Bruker FastScan Pro
FastScan Pro delivers automated high-speed AFM with nanometer precision for industry applications.
-
Bruker ForceRobot 400
ForceRobot offers reproducible, high-throughput single-molecule force measurements with nanometer accuracy.
-
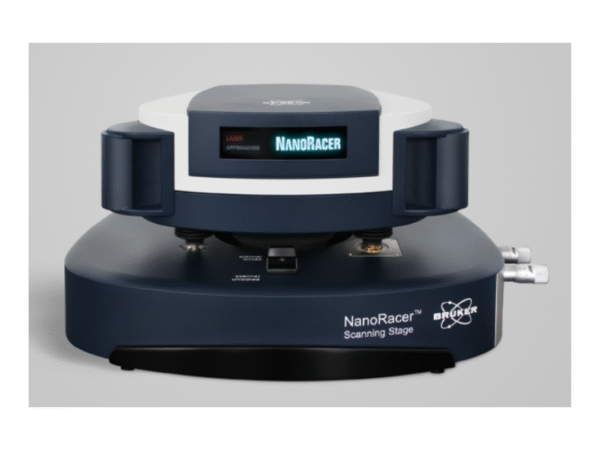
Bruker NanoRacer High-Speed AFM
NanoRacer enables ultrafast AFM imaging to study rapid dynamics in biological samples.
-
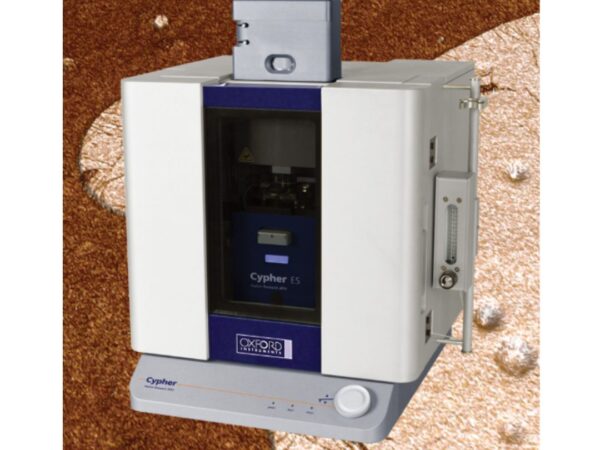
Oxford Instruments Cypher ES
Cypher ES Environmental AFM allows surface analysis under controlled conditions, ideal for environmental research and studies.
-
Oxford Instruments Cypher ES Battery Edition
Cypher ES Battery Edition AFM focuses on electrochemical analysis, optimizing studies of battery materials and reactions.
-
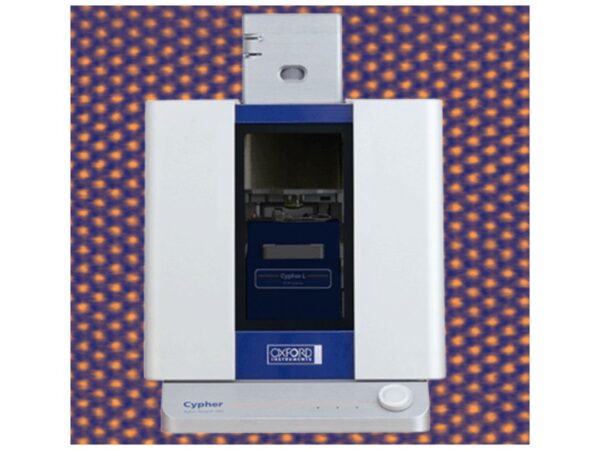
Oxford Instruments Cypher L
Cypher L AFM offers high-resolution imaging for surface analysis, delivering precise data for advanced research applications.
-
Oxford Instruments Cypher S
Cypher S AFM Microscope provides accurate surface and material analysis, designed for reliable and consistent performance.
-
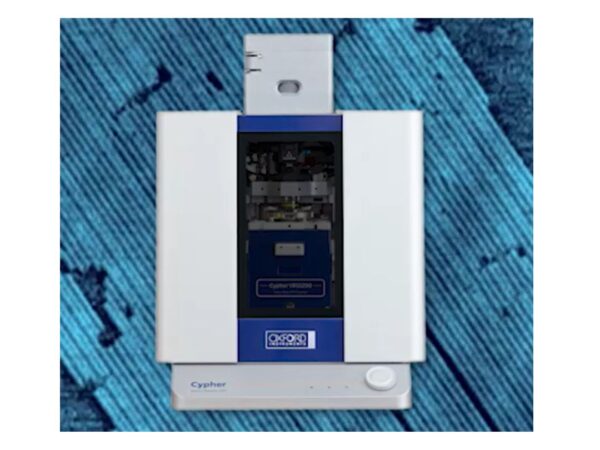
Oxford Instruments Cypher VRS1250
Cypher VRS1250 AFM delivers high-speed video-rate imaging, capturing dynamic processes with exceptional clarity and precision.
-
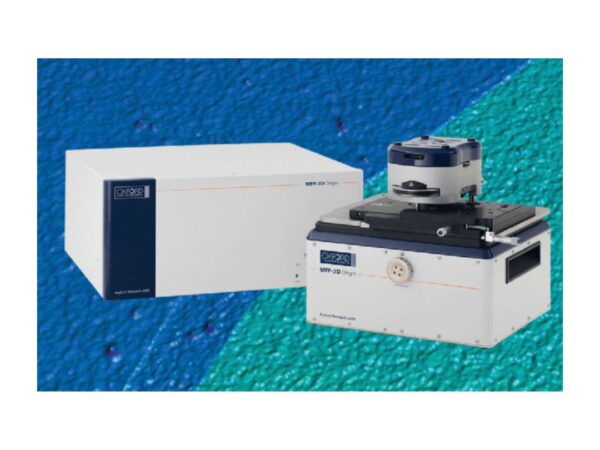
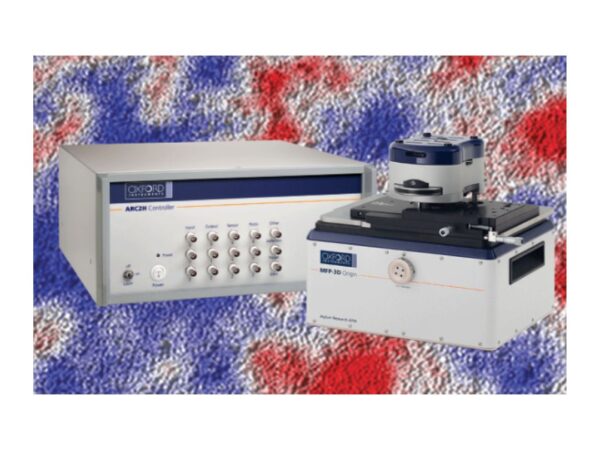
Oxford Instruments MFP-3D Origin
MFP-3D Origin AFM offers core scientific capabilities for reliable material analysis and advanced research.
-
Oxford Instruments MFP-3D Origin+
MFP-3D Origin Plus AFM enhances core AFM features with improved precision and application diversity.
-
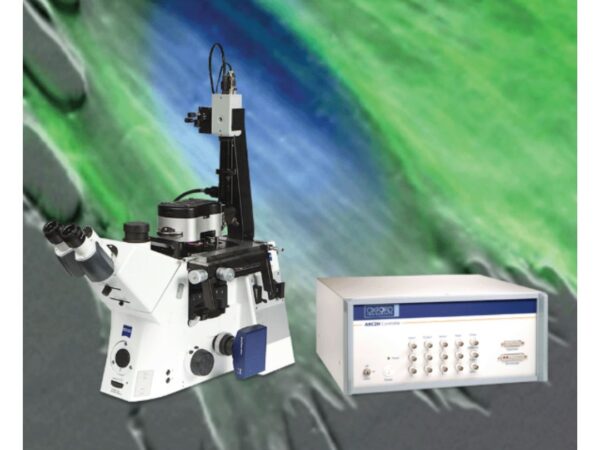
Oxford Instruments MFP-3D-BIO
MFP-3D Bio AFM specializes in soft, living sample analysis, making it ideal for biological and biomedical research.