Laser-Based Microarray Scanners
Laser-based microarray scanners are high-precision instruments used to detect and quantify fluorescence signals emitted from labeled DNA, RNA, or protein probes hybridized onto microarray slides. These systems typically employ one or more excitation lasers, commonly around 532 nm and 635 nm, to excite fluorophores such as Cy3 and Cy5, enabling simultaneous two-color detection. Advanced optics, photomultiplier tubes, and sensitive detectors convert emitted fluorescence into digital data with excellent resolution and a broad dynamic range. Because scanner performance can vary by design, standardized imaging protocols and consistent image-analysis software are essential for ensuring data comparability across instruments. Studies show that, when processed with uniform quantification workflows, results from different scanners are often highly comparable with minimal instrument-induced variation. Modern scanners also offer adjustable laser power, PMT gain, resolution settings, and automated focusing to optimize signal detection.read more
Key Features
- Laser-based microarray scanners provide sensitive fluorescence detection for labeled nucleic acids and proteins. They often support dual or multi-wavelength excitation, enabling simultaneous measurement of multiple dyes in a single scan.
- Most scanners are designed to read standard 1 × 3-inch microscope slides, including glass, coated glass, plastic, silicon, and gold-coated substrates. Support for widely used microarray formats ensures easy integration with existing laboratory workflows. This versatility allows consistent performance across different assay types and surface chemistries.
- Advanced models feature automated slide cassettes that enable continuous loading for high-throughput scanning. Raw data files can be automatically transferred into compatible analysis software, minimizing manual steps and reducing the risk of user error. These automated features significantly accelerate scanning workflows and improve overall laboratory productivity.
- Confocal detection systems help maintain accurate focal positioning across the entire slide, reducing background noise and enhancing signal-to-noise ratios. Real-time autofocus continuously follows slide curvature or movement, ensuring all regions remain sharply focused during scanning.
- Users can fine-tune laser power, detector gain, and focus parameters to optimize fluorescence detection for both weak and strong signals. High-bit-depth digitization and wide dynamic ranges allow accurate quantification across several orders of magnitude. This adaptability makes the scanners suitable for low-abundance targets without risking saturation of highly expressed features.
- Fast XY-stage motorization enables rapid image acquisition without compromising resolution. Adjustable scan speeds allow researchers to balance throughput with sensitivity depending on experimental needs. High-speed scanning supports large studies and routine workflows where time efficiency is critical.
- Many scanners integrate ozone-resistant features to prevent fluorophore degradation and maintain signal integrity. Built-in barcode readers ensure reliable sample tracking and traceability throughout the workflow. Several platforms are engineered to accommodate next-generation array densities and evolving microarray technologies, protecting long-term laboratory investment.
Applications of Laser-Based Microarray Scanners
- Gene expression analysis: Laser-based scanners quantify fluorescence from labeled cDNA to measure gene activity across thousands of targets simultaneously, enabling high-throughput transcriptomic profiling in research and clinical studies.
- Comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) and copy number variation analysis: By detecting differential hybridization signals, the scanners help identify genomic gains, losses, and structural alterations. These applications are essential for cancer genetics, cytogenetics, and inherited disorder analysis.
- SNP genotyping and genomic profiling: High-resolution fluorescence detection supports accurate identification of single-nucleotide polymorphisms across the genome. This enhances population genetics studies, disease-risk assessment, and precision medicine research.
- Protein and proteomic array imaging: Scanners are used to visualize and quantify fluorescently labeled proteins, antibodies, and antigens on microarray platforms, which enables detailed proteomic profiling and high-throughput analysis of protein interactions.
- Fluorescent biomarker detection for cancer and disease research: Their ability to measure low-abundance fluorescence makes them ideal for detecting disease-specific biomarkers. This supports oncology research, early diagnosis efforts, and therapeutic development.
- Pathogen detection and clinical microarray diagnostics: Fluorescence-based detection of microbial nucleic acids enables rapid identification of pathogens in research or diagnostic settings. These scanners also support IVD-compliant workflows for gene expression and infectious disease assays.
- High-throughput screening in pharma and biotech: Microarray scanners accelerate drug-discovery assays by enabling simultaneous quantification of thousands of molecular interactions, supporting target validation, lead optimization, and toxicity profiling.
- Core facility and multi-user microarray applications: Their speed, sensitivity, and multi-color imaging capabilities make them ideal for shared research facilities. They support routine studies such as transcriptomics, proteomics, and fluorescent biomarker assays.
- Infrared and fluorescent protein microarrays: Some scanners also support high-throughput IR microarrays for proteomic and immunoassay applications. This allows interference-free detection, improved sensitivity, and compatibility with infrared Western blot analysis.
- Advanced microarray studies and quantitative signal analysis: The instruments are used for basic research through advanced multi-omics studies involving fluorescence quantification across a wide dynamic range. Precise signal measurement enables robust statistical analysis and reproducible data across laboratories.
Showing 1–12 of 32 results
Category
- Bioreactors+
- Parallel Bioreactors
- Single-Use Bioreactors
- Stirred-Tank Bioreactors
- Capillary Electrophoresis Instruments+
- Capillary Gel Electrophoresis (CGE)
- Capillary Isoelectric Focusing (CIEF)
- Capillary Zone Electrophoresis (CZE)
- Cell Counters and Analyzers+
- Automated Cell Counters
- Manual Cell Counters
- Cellular Imaging Systems+
- Fluorescence Imaging Systems
- High-Content Imaging Systems
- Live-Cell Imaging Systems
- Centrifuges+
- Benchtop Centrifuges
- Clinical Centrifuges
- Micro Centrifuges
- Refrigerated Centrifuges
- Ultracentrifuges
- Chromatography Instruments+
- Gas Chromatography
- Ion Chromatography
- Liquid Chromatography
- Flow Cytometer+
- Cell Analyzers
- Cell Isolation Systems
- Cell Sorters
- High-Throughput Flow Cytometers
- Imaging Flow Cytometry
- Personal Flow Cytometers
- Portable/Benchtop Flow Cytometers
- Spectral Flow Cytometers
- Laboratory Incubators+
- CO2 Incubators
- Dry Bath Incubators
- Hypoxia Incubators and Chambers
- Incubator Shakers
- Laboratory Ovens
- Portable Incubators
- Thermal Mixers
- Laboratory Microscopes+
- Atomic Force Microscopes (AFM)
- Automated Modular Microscopes
- Compound Microscopes
- Confocal Microscopes
- Digital Microscopes
- Fluorescence Microscopes
- Inverted Microscopes
- Live Cell Imaging Microscopes
- Metallurgical Microscopes
- Multiphoton Microscopes
- Polarizing Microscopes
- Raman Microscopes
- Scanning Electron Microscopes (SEM)
- Stereo Microscopes
- Super-Resolution Microscopes
- Transmission Electron Microscopes (TEM)
- Upright Microscopes (Neuroscience)
- Liquid Handlers+
- Automated Pipetting Systems
- Multi-Channel Liquid Handlers
- Robotic Liquid Handlers
- Variable Volume Pipetting Systems
- Mass Spectrometers+
- Ambient Ionization
- APCI MS
- ESI MS
- FT ICR MS
- ICP MS
- Orbi Trap MS
- Quadrupole MS
- Time-of-Flight MS
- Microarray Scanners+
- DNA Microarray Scanners
- Laser-Based Microarray Scanners
- Microplate Readers+
- Absorbance Microplate Readers
- Fluorescence Microplate Readers
- Luminescence Microplate Readers
- Multimode Microplate Readers
- Particle Counters and Analyzers+
- Airborne Particle Counters
- Laser Diffraction Analyzers
- Liquid Particle Counters
- Nanoparticle Analyzers
- Portable Particle Counters
- Remote Particle Counters
Brand
- ACCU-SCOPE
- Agilent
- Airmodus
- Alphasense
- Analytik Jena
- ARGO-HYTOS
- Arrayit
- Aurora Biomed Inc.
- Azure Biosystems
- Baker
- BD Biosciences
- Beckman Coulter
- Beijing Challen Biotechnology
- Binder
- Bio-Techne
- Biobase
- BioRad
- BMG Labtech
- Bruker
- Celestron
- Cellbox
- Centurion Scientific Ltd
- ChemoMetec
- CleanAir
- Cleatech
- Corning
- Countstar
- CS Instruments
- CUBIC
- Cytek Biosciences
- Cytena
- Cytiva
- Data Technologies
- Descase
- Electrolab Biotech
- Eppendorf
- Euromex
- Evident
- Fermex
- Fluke
- Formulatrix
- Getinge
- Gilson
- GPC Bio
- Haier Biomedical
- Hamilton Company
- Hettich
- Hitachi High-Tech
- Hudson Robotics Inc.
- Hydro
- INFORS HT
- Innopsys
- Jasco
- Jeiotech
- JEOL
- Kanomax
- Keyence
- KNAUER
- LAB-KITS
- Labomed
- Labwit
- Leco
- Leica
- Lighthouse
- Logos Biosystems
- LOSI
- Lumex Instruments
- Luminex
- Malvern Panalytical
- Meiji Techno
- Memmert
- Merck
- Mettler-Toledo International Inc.
- Miltenyi Biotec
- Molecular Devices
- Motic
- MP Filtri
- MSE (Medical and Scientific Equipment)
- NCI
- Nikon Instruments
- NuAire
- ORFLO Technologies
- Oxford Instruments
- PAMAS
- Particle Measuring Systems
- Particles Plus
- PBS Biotech
- PCE instruments
- PerkinElmer
- PharSol
- PHCbi
- Prior Scientific
- Promega
- Qiagen NV
- Revvity
- RION
- Sartorius
- SATAKE
- Sciex
- Sebia
- SETA
- Setra
- Shimadzu
- SIBATA
- Sigma Laborzentrifugen GmbH
- Solaris Biotech
- Solida Biotech
- Sony Biotechnology Inc.
- SPT Labtech Ltd
- Stratedigm Inc.
- Sysmex Corporation
- Tecan
- TES
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- TSI
- Waters
- Western States Machine Company
- ZEISS
- ZETRON
-
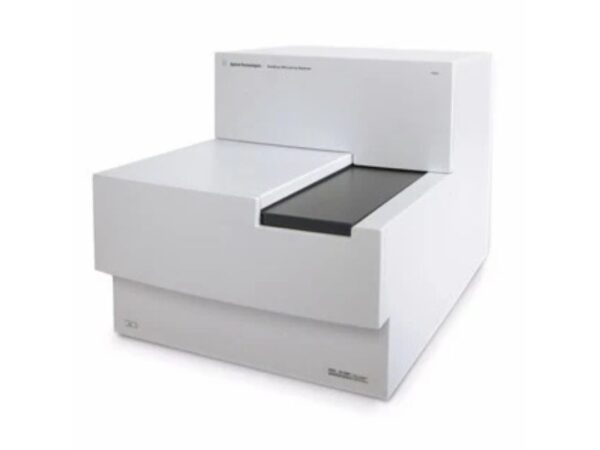
Agilent SureScan
The SureScan Microarray Scanner from Agilent delivers high-resolution scanning for CGH and SNP arrays, providing reliable data for genetic variation s...
-
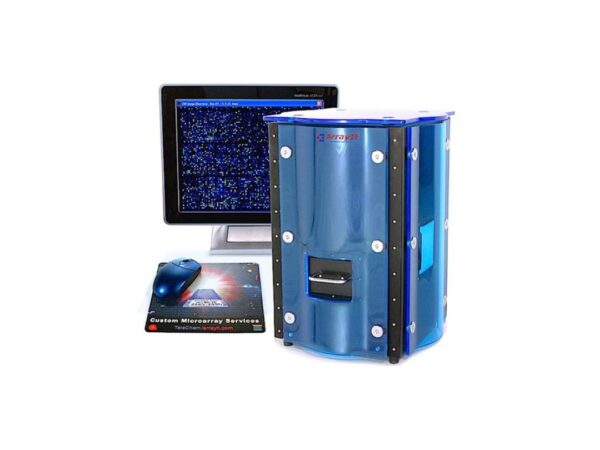
Arrayit Arrayit GenePix
Ensures compatibility with GenePix slides and protocols while providing high-resolution scanning and streamlined integration with fluorescence workflo...
-
Arrayit ArrayPix APXC
Streamlined microplate scanning with fluorescence or absorbance detection, perfect for rapid assay execution in research and pharma labs.
-
Arrayit ArrayPix APXCW
Delivers absorbance, luminescence, and fluorescence reading capabilities for multiple assay formats with intuitive software and fast results across bi...
-
Arrayit ArrayPix APXF
Designed for accurate and efficient scanning of standard microplates, ideal for HTS, drug discovery, and biochemical assay quantification.
-
Arrayit ArrayPix APXFW
Scans multiwell plates (96/384) for fluorescence or absorbance applications, ideal for high-throughput research or pharmaceutical assay screening.
-
Arrayit SpotLight 2 PWSL
Comprehensive support packages covering labor, parts, and diagnostics to ensure continuous uptime and reduce lab delays due to maintenance.
-
Arrayit SpotLight 2 SL2U
Flexible high-resolution scanning system designed to accommodate diverse microarray applications in R&D or diagnostic laboratories.
-
Arrayit SpotLight 2 SLMS
Provides cost-effective, high-resolution scanning of fluorescent microarrays, suitable for education, testing, and low-throughput workflows.
-
Arrayit SpotLight Blue SLMSB
Scanning solution for fluorescence-labeled DNA, RNA, and protein arrays with excellent resolution and sensitivity for research or diagnostic use.
-
Arrayit SpotLight Turbo PWSLT
Enables simultaneous detection of six fluorescent signals, ideal for multiplex experiments, pathway studies, and high-content analysis.
-
Arrayit SpotLight Turbo SLMST
The SpotLight scanner delivers high-resolution fluorescent microarray scanning for genomic and proteomic research with minimal background noise and in...